The Importance of Electrical Grounding for Safety and Efficiency
Electrical grounding is an important safety measure in any electrical system. It involves connecting parts of the electrical system to the Earth via a low-resistance path, effectively preventing harmful fault currents. Grounding plays a pivotal role in ensuring both human and equipment safety by diverting excess electrical energy and preventing electric shocks.
In addition to safeguarding individuals, proper grounding is essential for protecting electrical systems from damage. It provides a stable voltage level within the system, reducing the risk of voltage surges and preventing potential electrical fires. Proper grounding practices enhance the longevity and reliability of electrical devices and infrastructure.
Understanding the intricate process of electrical grounding might seem complex, but its importance cannot be overstated. By ensuring a secure path for electrical currents to dissipate safely, grounding mitigates the risks associated with electrical faults and overloads. This makes it an indispensable aspect of modern electrical engineering and safety.
Fundamentals of Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding ensures the safe operation of electrical systems by providing a path for electric current to follow in the event of a fault. This practice helps in preventing electrical shocks, equipment damage, and fires.
Concepts and Definitions
Grounding involves the physical connection of electrical circuits to the earth, which serves as a reservoir for dissipating electrical energy. The ground wire is the conductor that links an electrical system to the ground. Grounding creates a reference point for electrical currents, often referred to as “zero voltage”.
A crucial element of grounding is the grounding electrode. This is a rod or plate buried in the earth and connected to the system through the ground wire. Grounding ensures that if a fault occurs, the electricity will travel through the ground wire, rather than through someone’s body, reducing the risk of electric shock.
Importance of Grounding in Electrical Systems
Grounding plays an essential role in maintaining the safety and stability of electrical systems. It provides a safe path for electric current, preventing electrical hazards like shocks and fires. A well-grounded system protects people and equipment from potential harm.
In addition to safety, grounding helps in detecting and clearing ground faults. Ground faults occur when electrical current travels outside its intended path. A grounded system ensures that these faults are quickly identified and corrected, preserving the integrity of the electrical infrastructure.
Proper grounding also reduces electrical interference, ensuring the stable operation of sensitive electronic devices and communication systems. As such, effective grounding practices are vital for both residential and industrial applications. This broader protection and stability of systems underscore the importance of grounding in electrical networks.
Grounding and Electrical Safety
Grounding plays a crucial role in electrical safety by protecting individuals from electric shocks and preventing damage to electrical equipment. It provides a safe path for fault currents to flow into the earth and minimises risks associated with electricity.
Protection against Electric Shocks
Grounding protects individuals from electric shocks by providing a low-resistance path for fault currents to travel into the earth. When an electrical fault occurs, such as a short circuit, the grounding system ensures that the excessive current is safely redirected away from users and into the ground. This prevents the electric current from travelling through a person’s body, which can be fatal.
Devices like Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) are essential components in this safety framework. A GFCI detects even minor current leaks and shuts off the electrical circuit to prevent shocks. GFCIs are particularly important in areas with a higher risk of electrical hazards, such as bathrooms and kitchens. These devices offer an additional layer of protection by responding to inconsistencies in electrical current flow that may not trigger other safety mechanisms.
Preventing Equipment Damage
Proper grounding also protects electrical equipment from damage. Grounding systems dissipate excess electrical energy safely into the earth, which can occur due to faults or lightning strikes. This safe dispensation of excess energy prevents the accumulation of dangerous voltages, thus safeguarding equipment.
Electrical grounding ensures that any build-up of static electricity or fault current is efficiently managed. For instance, during a fault, grounding provides a controlled and predictable path for current to flow, reducing the risk of electrical fires. Equipment grounding helps maintain the operational integrity of devices, minimizing downtime, and extending the lifespan of electrical appliances.
By integrating thorough grounding practices and devices like GFCIs, both human safety and equipment longevity can be significantly enhanced.
Components of a Grounding System
A well-designed grounding system consists of several key components that ensure the safe and effective discharge of electrical energy. Each component has a specific role in maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical installations.
Grounding Wires and Rods
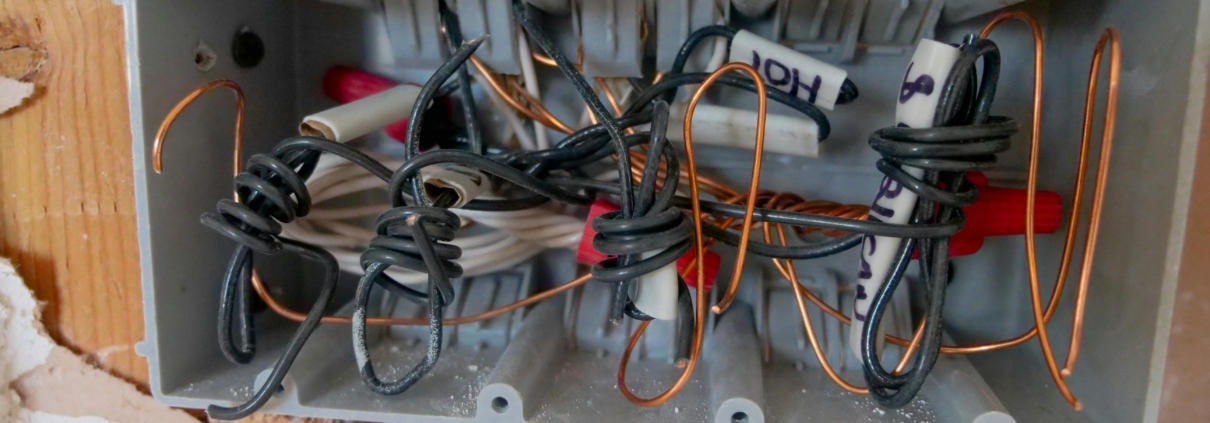
Grounding wires are essential in creating a low-resistance path for electrical currents to travel safely into the Earth. Constructed from conductive materials such as copper or aluminium, these wires connect various parts of an electrical system to grounding electrodes.
Grounding rods, often made from copper or galvanized steel, are driven into the ground to establish a physical connection with the Earth. These rods are chosen for their durability and high conductivity, which are crucial for efficient grounding. Proper installation depth and spacing of grounding rods are critical to achieving a solid connection with the Earth, reducing resistance and enhancing the grounding system’s overall performance.
Electrode Conductors and Connections
Electrode conductors are another vital component, tasked with linking the electrical system components to the grounding electrodes. Typically made from highly conductive materials like copper, these conductors must be sized correctly according to electrical codes and standards to handle potential fault currents efficiently.
Connections within a grounding system are paramount to its effectiveness. Secure and corrosion-resistant connections ensure long-term reliability. Techniques such as exothermic welding or mechanical clamps are commonly used to create robust and lasting joints. Proper maintenance and periodic inspections are necessary to prevent degradation over time, ensuring the grounding system continues to provide optimal safety and performance.
Installation and Types of Grounding
Electrical grounding is a critical component of safety and functionality in electrical installations. This section discusses the methods used to install grounding systems and the different forms of grounding techniques.
Methods of Ground Installation
Ground installations require specific techniques to ensure that the electrical systems are safely connected to the Earth. A typical method involves driving grounding electrodes into the ground. These electrodes provide a path for electrical currents to safely dissipate.
Another common method includes connecting the electrical system to a Ground Bus, which is then linked to grounding electrodes. This setup ensures that all parts of the system are effectively grounded. Proper installation is vital to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the correct operation of electrical devices.
Different Forms of Grounding
Grounding systems can be categorised into several types, each serving distinct purposes. An ungrounded system lacks a direct connection to the Earth, which can be useful in reducing electrical interference in specialised applications.
A solidly grounded system features a direct connection between the electrical system and the ground, providing a secure path for fault currents. Resistance grounding, which includes both low and high resistance grounding, limits fault current by introducing a resistor between the system and ground.
Reactance grounding uses reactors to limit fault currents, while resonant grounding employs tuned elements to reduce transient over-voltages. Each type is selected based on the specific safety and operational requirements of the facility.
Grounding in Residential and Commercial Settings
The safety and functionality of electrical systems in residences and commercial buildings heavily rely on proper grounding. This ensures that electrical currents have a safe path to follow, preventing potential hazards and protecting both people and equipment.
Domestic Electrical Systems
In residential settings, grounding is crucial for protecting against electrical shocks. Each home typically has a grounding system comprising a grounding electrode, often a metal rod driven into the earth. This is connected to the home’s electrical system via the grounding conductor.
- Grounding ensures that in the event of a fault, the excess electrical current is safely directed into the earth.
- This protective measure stabilises the voltage levels in the home, preventing damage to electrical equipment.
Grounding also helps safeguard against electrical fires caused by faults in circuits. Homeowners should regularly inspect grounding connections to ensure they are secure and up to code.
Commercial and Industrial Grounding Standards
Commercial and industrial environments have more complex grounding needs due to higher power demands and extensive electrical circuits. Grounding in these settings involves connecting grounding electrodes back to the building’s electrical service via a grounding electrode conductor (GEC).
- Grounding stabilises voltage levels, ensuring the efficient operation of electrical equipment and reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Compliance with standards, such as those set by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), is essential for safety.
Regular maintenance and inspection of grounding systems are critical to address any potential issues before they lead to significant problems. Effective grounding in commercial and industrial settings supports the overall safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
Electrical Grounding and Electronic Equipment
Electrical grounding is crucial in protecting electronic equipment from electrical interference and ground loops, which can damage sensitive devices.
Electrical Interference and Ground Loops
Electrical interference affects the performance of electronic equipment by introducing unwanted signals. Ground loops, a common cause of interference, occur when multiple ground paths are established, creating a loop. This can induce electromagnetic interference (EMI), leading to noise and signal degradation.
To mitigate ground loops, a single grounding point is recommended. This reduces the likelihood of interference. Proper shielding and cabling techniques also help in maintaining cleaner signals and efficient operation of the equipment. Minimising these issues ensures the longevity and reliability of electronic systems.
Grounding for Sensitive Electronic Devices
Sensitive electronic devices require meticulous grounding to avoid damage or malfunction. Devices like medical equipment, precision instruments, and communication systems are particularly vulnerable. Improper grounding can lead to voltage surges and data loss.
Using isolated grounding techniques is essential. This involves connecting the equipment to a dedicated ground that is separate from other electrical systems. Employing surge protectors and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) can provide additional layers of protection.
In industrial environments, the grounding of sensitive equipment ensures that operational noise is minimised, maintaining the integrity of data processing and communication systems. This approach is vital for the safe and effective operation of critical electronic devices.
Understanding Earth and Ground Potential
The concepts of earth ground and electrical potential are crucial for the safety and functionality of electrical systems. These concepts help in mitigating the risks associated with electrical faults and ensure the smooth operation of electrical equipment.
Path to Earth and Potential Differences
Electrical systems need a reliable path to earth to safely dissipate unwanted electrical energy. This is achieved by connecting a grounding wire to a grounding electrode, such as a metal rod or a ground plate, which is buried in the earth. By providing a conductive path, the electrical energy is transferred from the system to the earth, maintaining a consistent ground potential.
To ensure an effective path to ground, the connection must be secure and low-resistance. Any breaks or high resistance in the grounding path can lead to potential differences, which might cause dangerous malfunctions or electrical shocks. Proper grounding also helps to stabilise the voltage levels in the electrical system.
Electrical Potential and Safety Concerns
Electrical potential refers to the voltage relative to a common reference point, typically the earth ground. The earth is considered at zero volts, providing a universal reference point for all other voltages in the system. This helps in maintaining consistent voltages across the electrical network and reducing the risk of electrical shocks.
Safety concerns arise when there’s a significant voltage difference between the ground and the electrical equipment. Without proper grounding, these potential differences can become hazardous, leading to electrical shocks or damage to the equipment. Ensuring that all parts of the electrical system are properly grounded minimises these risks and enhances safety.
In summary, understanding the path to earth and managing potential differences is essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Proper grounding plays a critical role in achieving this by stabilising electrical potentials and preventing dangerous voltage levels.
Grounding and the Power Grid
Grounding is essential in the power grid, ensuring the safety and stability of power lines, distribution networks, and power generation systems. Proper grounding helps protect both equipment and personnel from electrical faults and surges.
Power Line and Distribution Safety
Grounding in power lines and distribution networks is crucial for maintaining electrical energy flow and preventing hazardous situations. By connecting the system to the earth, grounding provides a controlled path for electrical faults. This reduces the risk of electrical shock and mitigates fire hazards caused by lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions.
Power distribution systems use various grounding methods. These include connecting metallic components such as transformers and circuit breakers to the grounding network. This ensures any fault currents are safely diverted to the earth. Additionally, grounding helps in maintaining stable voltage levels, preventing voltage spikes that can damage sensitive equipment.
Grounding in Power Generation and Transmission
Grounding in power generation and transmission systems plays a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electrical energy production. At power plants, equipment like generators and transformers are grounded to manage excess electricity and prevent equipment damage.
In the context of transmission, grounding facilitates the safe transfer of high-voltage electricity across long distances. For instance, substation grounding systems consist of grounding networks and connections to the earth. These networks bond all equipment frames and metallic structures in the substation, offering a secure path for fault currents.
Furthermore, grounding in transmission systems ensures any fault can be quickly detected and cleared, maintaining the integrity and stability of the electrical grid. Grounding practices also protect personnel working on or near these high-voltage systems by minimising the risk of electric shock.
Grounding Techniques and Best Practices
Grounding techniques and best practices ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. This section explores the industry standards and regulations, along with effective grounding strategies.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Grounding practices are guided by several industry standards and regulations. The Central Electricity Authority Regulations mandate proper grounding to ensure safe operation. These regulations call for regular inspections and maintenance of grounding systems, which helps in preventing hazards.
Electrical systems must adhere to specific guidelines like the use of grounding conductors that meet defined electrical and mechanical properties. For example, metallic parts of machinery must be connected to create a low-impedance path to the ground, reducing the risk of electrical shock. Compliance with these standards aids in protecting both personnel and equipment, ensuring operational stability and safety.
Effective Grounding Strategies
Implementing effective grounding strategies involves several key techniques. One such method is the installation of multiple ground rods, spaced at least twice the length of the rods apart, to improve the efficiency of the ground connection. In areas with poor soil conditions, deep-driven or chemically enhanced ground rods are recommended to achieve better conductivity.
Connecting conducting objects to a common reference point or to the Earth, which is the essence of grounding, ensures device safety and the prevention of electrical interference. Additionally, using low-impedance connections enhances the likelihood of detecting and clearing ground faults, protecting both people and the electrical systems.
By following these methods, one can achieve a robust grounding system that provides reliable safety and operational efficacy.
Grounding and Lightning Protection
Proper grounding and lightning protection are crucial for safeguarding structures and electrical systems from the immense energy of lightning strikes. The focus here is on understanding the impact of lightning on structures and how the effective design of lightning protection installations can mitigate these risks.
Impact of Lightning on Structures and Systems
Lightning strikes can unleash vast amounts of energy in an instant, causing severe damage to buildings and electrical systems. When a lightning bolt strikes, it seeks the path of least resistance to the ground.
Without adequate lightning grounding, the energy can cause fires, structural damage, and electrical surges.
Electrical systems are particularly vulnerable. The high voltage can lead to catastrophic failures in equipment, corrupting data and damaging components. Proper grounding helps disperse the energy safely into the earth, reducing the risk of these destructive outcomes.
In residential or commercial buildings, poor grounding can lead to widespread electrical malfunctions and pose significant safety hazards to occupants.
Design of Lightning Protection Installations
Effective lightning protection systems are essential for mitigating the risks associated with lightning strikes on buildings and other structures. These systems often involve a network of air terminals, conductors, and ground connections designed to intercept and channel lightning’s energy safely into the ground.
Air terminals, commonly known as lightning rods, are positioned at high points on a structure to capture lightning strikes.
Conductors then provide a low-resistance path, directing the energy towards the ground.
Properly designed grounding systems, including the use of grounding electrodes, ensure that the immense energy is absorbed safely into the earth. To achieve maximum efficiency, the connections must be short and direct, minimising inductance and ensuring rapid dissipation of energy.
Implementing these designs helps safeguard both structural integrity and the functionality of electrical systems during electrical storms.